Blockchain Beyond Crypto: 4 Enterprise Supply Chain Apps 2025

Blockchain technology is rapidly evolving beyond its cryptocurrency origins, now poised to revolutionize enterprise supply chains by 2025, promising enhanced transparency, efficiency, and security through four innovative applications.
The landscape of global commerce is on the cusp of a significant transformation, as Demystifying Blockchain Beyond Crypto: 4 Enterprise Applications Set to Revolutionize Supply Chains in 2025 (INSIDER KNOWLEDGE) reveals a powerful shift in how goods are tracked, verified, and managed. This emerging trend moves blockchain squarely into critical business operations, promising unprecedented levels of transparency and efficiency.
The Shift: Blockchain’s Enterprise Evolution
Blockchain, once primarily associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is now rapidly gaining traction as a foundational technology for enterprise solutions. This evolution is driven by its inherent properties of immutability, transparency, and decentralization, which address long-standing challenges within complex global supply chains.
As of late 2024, major corporations and tech innovators are heavily investing in blockchain infrastructure, signaling a definitive move beyond speculative digital assets. The focus has shifted to practical applications that can deliver tangible benefits in real-world scenarios, particularly in sectors where trust and verifiable data are paramount.
Why Enterprises are Adopting Blockchain
Enterprises are increasingly turning to blockchain for several compelling reasons. The technology offers a robust framework for creating shared, immutable records across disparate entities, fostering a new era of collaborative trust without relying on a central authority.
- Enhanced Transparency: Provides a single, verifiable source of truth for all participants.
- Improved Efficiency: Automates processes and reduces reconciliation efforts.
- Increased Security: Cryptographic security protects data from tampering.
- Reduced Costs: Minimizes intermediaries and operational overhead.
Application 1: End-to-End Traceability and Provenance
One of the most immediate and impactful applications of blockchain in supply chains is providing unparalleled end-to-end traceability. This capability allows every product to be tracked from its origin through manufacturing, transit, and ultimately to the consumer, creating a complete and immutable digital history.
For industries grappling with counterfeiting, ethical sourcing, or regulatory compliance, this level of transparency is revolutionary. Consumers, too, benefit from the ability to verify product authenticity and understand its journey, fostering greater trust in brands.
Real-time Tracking and Data Verification
Blockchain-based traceability systems integrate with IoT devices and sensors at various points in the supply chain. These devices record data such as location, temperature, and handling conditions directly onto the blockchain, ensuring that information is accurate, timely, and tamper-proof.
This real-time data flow enables proactive problem-solving, such as identifying delays or quality deviations before they escalate. For example, a pharmaceutical company can monitor the temperature of sensitive vaccines throughout their entire journey, ensuring efficacy and safety upon delivery.
Application 2: Smart Contracts for Automated Logistics
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In the context of supply chains, these contracts automatically trigger actions when predefined conditions are met, eliminating manual intervention and accelerating processes.
By 2025, smart contracts are projected to automate a vast array of logistics operations, from payment releases upon delivery confirmation to insurance payouts for damaged goods. This automation reduces administrative burdens, minimizes disputes, and significantly speeds up transaction cycles.
Streamlining Payments and Compliance
Consider international shipping, where numerous parties and complex documentation are involved. A smart contract can automatically release payment to a supplier once goods are verified as received at a port, or disburse funds to a customs broker upon successful clearance. This eliminates delays associated with manual invoicing and approvals.
- Automated Payments: Funds released instantly upon condition fulfillment.
- Faster Settlements: Reduces payment cycles from weeks to days or even hours.
- Reduced Disputes: Objective, code-enforced agreements minimize disagreements.
- Regulatory Adherence: Can embed compliance rules, ensuring automatic adherence.
Application 3: Enhanced Supply Chain Finance and Trade
Blockchain technology is poised to transform supply chain finance by providing greater transparency and reducing risk for all participants. Traditional trade finance often involves complex, paper-intensive processes that are slow and expensive, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
By digitizing assets and creating a shared ledger of transactions, blockchain facilitates more efficient and accessible financing options. This can unlock capital for suppliers, improve cash flow, and reduce the cost of trade for everyone involved in the supply chain.
Tokenization of Assets and Invoice Financing
One key innovation is the tokenization of assets, where physical goods or invoices are represented as digital tokens on a blockchain. These tokens can then be easily traded or used as collateral for financing. For instance, a manufacturer’s invoice can be tokenized and sold to a financier for immediate payment, providing instant liquidity.
This system offers greater visibility into the underlying assets and transactions, making it easier for financial institutions to assess risk and offer more favorable terms. It effectively democratizes access to finance, especially for suppliers in developing nations who may struggle with traditional banking systems.
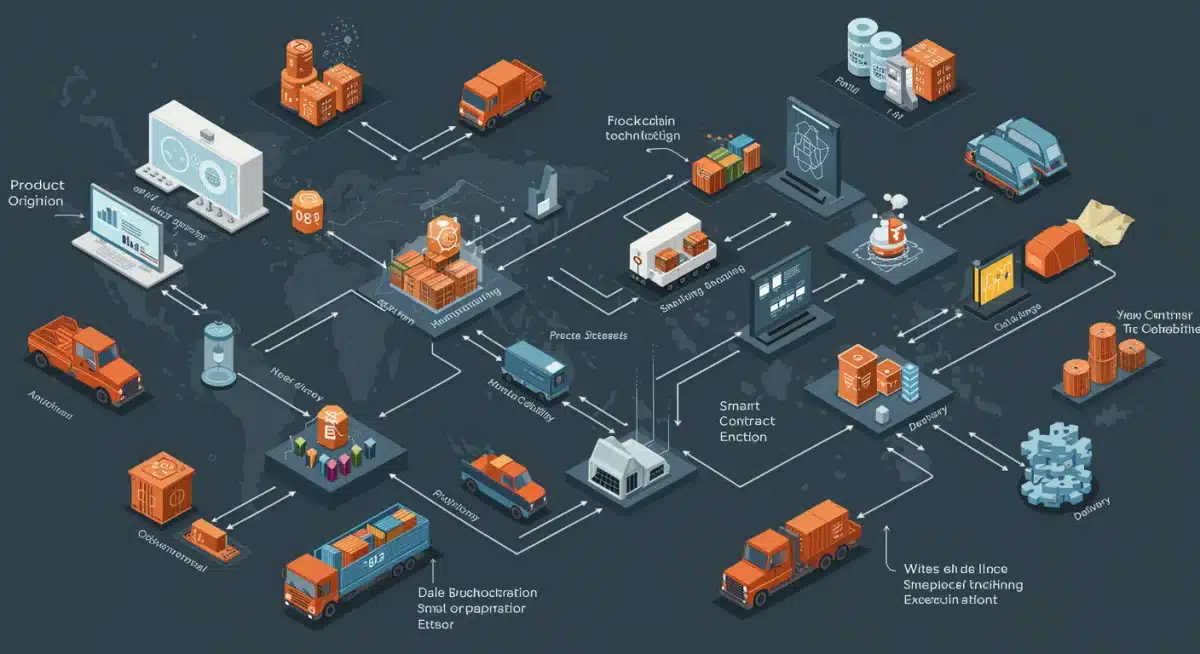
Application 4: Decentralized Identity and Data Sharing
The concept of decentralized identity (DID) on a blockchain allows entities—whether individuals, businesses, or devices—to control their own digital identities and share verifiable credentials securely. In supply chains, this translates to improved data sharing and authentication without relying on centralized authorities.
This application is critical for ensuring that only authorized parties access sensitive information, verifying the identity of suppliers and partners, and maintaining data integrity across the entire network. It addresses concerns around data privacy and security, which are paramount in today’s interconnected world.
Secure Collaboration and Trust Networks
With DID, each participant in a supply chain can maintain a sovereign digital identity. When a manufacturer needs to verify a supplier’s certifications or an auditor needs to access production records, these credentials can be shared directly and securely through the blockchain, without revealing unnecessary information to third parties.
This fosters a network of trust where data sharing is permissioned and verifiable, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. It also simplifies compliance audits and ensures that all parties are operating within agreed-upon standards, strengthening the overall integrity of the supply chain ecosystem.
Challenges and the Path Forward for Blockchain Adoption
While the potential of blockchain in supply chains is immense, its widespread adoption is not without challenges. Interoperability between different blockchain platforms, regulatory clarity, and the need for standardized protocols remain significant hurdles. Furthermore, the initial investment in technology and the cultural shift required within organizations can be substantial.
However, industry consortiums and leading technology providers are actively working to address these issues. Initiatives focused on creating common standards and building user-friendly interfaces are paving the way for easier integration. Education and pilot programs are also crucial in demonstrating the practical benefits and overcoming resistance to change, accelerating the transition to blockchain-powered supply chains.
| Key Application | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| End-to-End Traceability | Tracks products from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and transparency with immutable records. |
| Smart Contracts | Automates logistics and payment processes based on predefined conditions, reducing manual intervention and delays. |
| Supply Chain Finance | Enhances financing options and liquidity by tokenizing assets and invoices, lowering risk for all parties. |
| Decentralized Identity | Enables secure, permissioned data sharing and authentication, improving privacy and trust across the network. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Blockchain in Supply Chains
Blockchain’s primary benefit is enhanced transparency and traceability. It creates an immutable record of every transaction and movement, allowing all participants to verify product origins, journey, and authenticity, significantly reducing fraud and improving accountability.
Smart contracts automate logistics by executing predefined actions when specific conditions are met. This can include automatic payment releases upon delivery, triggering insurance claims, or updating inventory, thereby speeding up processes and reducing manual errors and disputes.
Yes, blockchain significantly improves supply chain finance by tokenizing assets like invoices, making them easily tradable and accessible for financing. This provides better liquidity for suppliers, reduces financing costs, and increases trust among financial institutions and businesses.
Decentralized identity (DID) allows participants in a supply chain to control their own digital identities and share verifiable credentials securely. It ensures that only authorized entities access sensitive data, enhancing privacy, security, and trust across the network without central oversight.
Key challenges include interoperability issues between different blockchain platforms, the need for clearer regulatory frameworks, and significant initial investment. Overcoming these requires industry collaboration, standardization efforts, and robust pilot programs to demonstrate tangible ROI.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Blockchain in Enterprise
The trajectory for blockchain’s integration into enterprise supply chains is steep and accelerating. As of late 2024, the groundwork for these revolutionary applications is firmly in place, with significant pilot programs and early implementations already demonstrating substantial benefits. Expect to see continued investment in interoperability solutions and standardized frameworks, which will be crucial for scaling these technologies across diverse industries. The coming years will witness a profound shift towards more resilient, transparent, and efficient global supply networks, driven by the immutable power of blockchain.