Biometric Security 2025: Comparing 5 Leading Technologies

Five leading biometric security technologies are currently redefining authentication as of 2025, offering enhanced protection against evolving digital threats and shaping the future of secure access across various sectors.
The landscape of digital security is rapidly evolving, with advanced authentication methods becoming crucial. In 2025, the focus on biometric security 2025 is intensifying as organizations and individuals seek more robust and convenient ways to protect sensitive data and access. This report delves into the five leading biometric technologies poised to dominate the market, offering a critical comparison of their capabilities and potential impacts.
The Rise of Biometric Authentication in 2025
Biometric authentication, once a concept confined to science fiction, has become a cornerstone of modern security infrastructure. Its ability to verify identity based on unique biological and behavioral characteristics offers a significant leap beyond traditional passwords and PINs. As of early 2025, the global push for seamless yet impenetrable security has accelerated the adoption and refinement of various biometric modalities.
The increasing sophistication of cyber threats necessitates a move towards authentication methods that are harder to compromise. Biometrics provides this enhanced layer of security, reducing vulnerabilities associated with forgotten or stolen credentials. This shift is not merely about convenience; it is about building a more resilient digital ecosystem.
Driving Factors for Biometric Adoption
Several key factors are propelling the widespread integration of biometric systems across industries. These include consumer demand for easier access, regulatory pressures for stronger data protection, and technological advancements making these systems more accurate and affordable.
- Enhanced Security: Biometrics are inherently difficult to replicate or steal, offering superior protection against fraud.
- User Convenience: Eliminating the need for complex passwords improves user experience and reduces login friction.
- Regulatory Compliance: New data protection regulations often encourage or mandate stronger authentication measures.
- Technological Maturity: Improved sensors, AI algorithms, and processing power have made biometrics more reliable.
Fingerprint Recognition: A Familiar Frontrunner
Fingerprint recognition remains one of the most widely adopted and recognizable biometric technologies in 2025. From unlocking smartphones to authorizing financial transactions, its pervasive presence speaks to its reliability and user acceptance. The technology has matured significantly, moving beyond simple optical scans to more sophisticated capacitive and ultrasonic methods.
Capacitive sensors detect variations in electrical current caused by the ridges and valleys of a fingerprint, while ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to create a highly detailed 3D map of the print. These advancements have made fingerprint recognition more resistant to spoofing attempts using molds or replicas, although challenges persist with damaged or obscured prints.
Advancements in Fingerprint Technology
Recent innovations focus on integrating fingerprint scanners directly into screens and improving liveness detection. This ensures that the scanned print belongs to a living person, not a static image or mold.
- Under-Display Scanners: Seamlessly integrated into smartphone and device screens for a sleek design.
- Liveness Detection: Algorithms analyze subtle biological signs to prevent spoofing with fake fingerprints.
- Multi-Factor Integration: Often combined with PINs or facial recognition for enhanced security layers.
- Edge Computing: Processing fingerprint data locally on the device for faster authentication and privacy.
Facial Recognition: Evolving Accuracy and Privacy Concerns
Facial recognition technology has seen rapid advancement and widespread deployment in 2025, particularly in areas like access control, identity verification, and public security. Modern systems leverage sophisticated AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze unique facial features, including inter-eye distance, nose shape, and jawline contours. The accuracy of these systems has reached unprecedented levels, even performing well in varying lighting conditions and with partial obstructions.
Despite its technical prowess, facial recognition continues to be a subject of intense debate regarding privacy and ethical implications. Concerns revolve around mass surveillance capabilities, potential for bias in algorithms, and the storage of sensitive biometric data. Balancing security benefits with individual rights remains a critical challenge for developers and policymakers.
Key Challenges and Solutions
Addressing privacy concerns and improving algorithmic fairness are paramount for broader public acceptance. Solutions involve anonymization techniques and robust data governance frameworks.
- Bias Mitigation: Developing algorithms trained on diverse datasets to reduce demographic bias.
- Privacy-Preserving Techniques: Using techniques like homomorphic encryption for secure data processing.
- 3D Liveness Detection: Employing 3D cameras and infrared sensors to distinguish live faces from photos or masks.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing clear laws and guidelines for the ethical deployment of facial recognition.
Iris and Retina Scans: Unparalleled Precision
Iris and retina scans represent the pinnacle of biometric precision in 2025, offering extremely high accuracy rates due to the unique and stable patterns within the human eye. The iris, the colored part of the eye, contains intricate patterns that are unique to each individual and remain unchanged throughout life. Retina scans, though less common, analyze the unique pattern of blood vessels at the back of the eye, providing another highly secure identifier.
These technologies are primarily deployed in high-security environments such as data centers, airports, and government facilities where uncompromising authentication is critical. While highly accurate, the scanning process can be perceived as less convenient than fingerprint or facial recognition, requiring specific positioning and lighting conditions. However, their reliability often outweighs these minor inconveniences in critical applications.
Applications in High-Security Sectors
The inherent stability and uniqueness of iris and retina patterns make them ideal for scenarios demanding the highest level of identity assurance.
- Border Control: Expediting secure passage at international checkpoints.
- Critical Infrastructure Access: Protecting sensitive facilities like power plants and nuclear sites.
- Healthcare Data Security: Controlling access to confidential patient records.
- Financial Institutions: Securing high-value transactions and vault access.
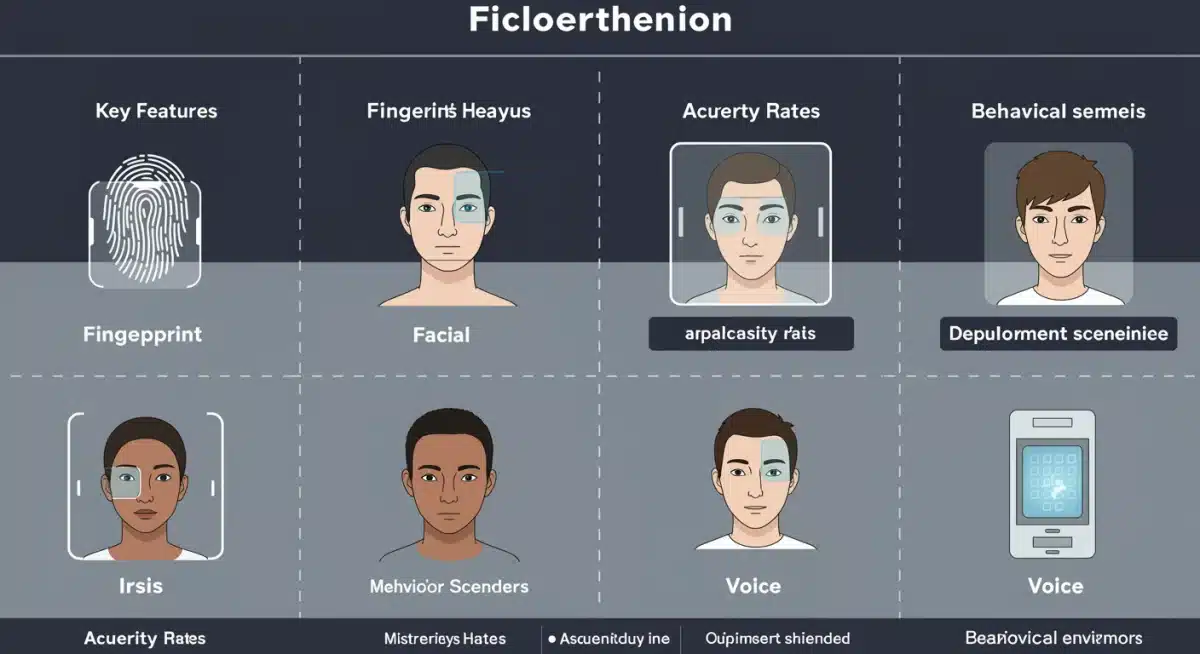
Voice Authentication: The Power of the Human Voice
Voice authentication, also known as voice biometrics, is gaining significant traction in 2025 as a convenient and accessible method for verifying identity. This technology analyzes unique characteristics of an individual’s voice, including pitch, tone, accent, and speech patterns, to create a voiceprint. Unlike speech recognition, which identifies what is being said, voice authentication focuses on who is speaking.
Its primary applications include customer service hotlines, banking transactions, and smart home device control, where hands-free authentication is highly desirable. Recent advancements in AI and machine learning have significantly improved its accuracy, making it more robust against impersonations and background noise. However, challenges remain with voice changes due to illness, aging, or intentional disguise, requiring sophisticated liveness detection.
Overcoming Voice Authentication Challenges
To enhance reliability, modern voice authentication systems integrate anti-spoofing measures and continuous verification techniques.
- Anti-Spoofing: Detecting recordings or synthesized voices through subtle acoustic analysis.
- Phrase Prompts: Using dynamic phrases to ensure a live, active response.
- Continuous Authentication: Verifying identity throughout a conversation, not just at the start.
- Noise Cancellation: Advanced algorithms to filter out background noise for clearer voiceprints.
Behavioral Biometrics: The Future of Continuous Authentication
Behavioral biometrics represents a cutting-edge frontier in biometric security 2025, focusing on the unique ways individuals interact with their devices. Instead of static physical traits, this technology continuously analyzes patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, gait, and even how a user holds their phone. This creates a dynamic, evolving profile that is incredibly difficult for imposters to replicate. It operates silently in the background, providing passive and continuous authentication.
This approach offers a significant advantage by constantly verifying identity without explicit user action, making it ideal for preventing account takeover fraud and detecting suspicious activity in real-time. While still in its nascent stages compared to other biometrics, behavioral biometrics holds immense promise for enhancing security without compromising user experience, offering a seamless and invisible layer of protection.
Applications and Advantages
The continuous nature of behavioral biometrics makes it particularly effective for proactive fraud detection and long-session security.
- Fraud Detection: Identifying anomalous behavior that might indicate an account compromise.
- Continuous Verification: Maintaining authenticated status throughout a session without repeated logins.
- User Experience: Invisible authentication that doesn’t interrupt workflow.
- Adaptability: Profiles adapt over time, learning legitimate changes in user behavior.
Comparative Analysis and Future Outlook
Each of the five leading biometric technologies—fingerprint, facial, iris, voice, and behavioral—offers distinct advantages and faces unique challenges in 2025. While fingerprint and facial recognition provide a balance of convenience and security for mass market adoption, iris and retina scans continue to excel in high-security environments due to their unparalleled precision. Voice authentication offers hands-free convenience, and behavioral biometrics promises continuous, invisible security.
The future of biometric security 2025 is not about a single dominant technology but rather a convergence of multiple modalities. Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems that combine several biometric methods with traditional credentials, creating highly resilient security frameworks. This layered approach mitigates the weaknesses of individual biometrics and enhances overall security posture.
As technology progresses, expect further integration of AI and machine learning to improve accuracy, liveness detection, and anti-spoofing capabilities across all biometric types. The focus will also shift towards privacy-enhancing technologies and robust regulatory frameworks to build public trust and ensure ethical deployment of these powerful tools.
| Biometric Technology | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Fingerprint Recognition | Widespread adoption and user familiarity, improved under-display tech. |
| Facial Recognition | High accuracy with AI, evolving for diverse conditions, widespread use. |
| Iris/Retina Scans | Unparalleled precision and stability, ideal for high-security environments. |
| Behavioral Biometrics | Continuous, passive authentication for real-time fraud detection. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Biometric Security
The primary benefit of biometric security in 2025 is enhanced security combined with improved user convenience. Biometrics offer a more robust defense against unauthorized access compared to traditional methods, simultaneously streamlining the authentication process for users across various platforms and devices.
Behavioral biometrics identify individuals based on unique patterns of interaction, such as typing rhythm or mouse movements, providing continuous authentication. Physical biometrics, like fingerprints or iris scans, rely on static biological traits for one-time verification, offering different security advantages.
Yes, privacy concerns with facial recognition are actively being addressed. Developers are implementing privacy-preserving techniques like data anonymization and homomorphic encryption. Additionally, regulatory bodies are establishing stricter guidelines and ethical frameworks to govern its deployment, aiming to balance security with individual privacy rights.
Iris and retina scans generally offer the highest precision among biometric technologies. Their intricate and stable patterns provide an extremely unique identifier, making them ideal for high-security applications where accuracy is paramount and false positives are unacceptable, although they can be less convenient for everyday use.
It is unlikely that a single biometric method will dominate in the future. The trend in 2025 is towards multi-factor authentication, combining several biometric modalities with other security measures. This layered approach enhances overall security by mitigating the individual weaknesses of any single biometric technology and adapting to diverse use cases.
What Happens Next
The trajectory of biometric security in 2025 indicates a future where integrated, multi-modal systems become the standard. Expect to see continued research into anti-spoofing mechanisms and liveness detection across all biometric types, driven by the escalating sophistication of cyber threats. Policy and ethical discussions will also intensify, shaping how these powerful technologies are deployed responsibly. The focus will be on creating seamless, secure, and privacy-respecting authentication experiences that adapt to the user’s context and risk profile, ultimately redefining trust in the digital age.