AI Integration in US Manufacturing: 2025 Productivity Boost?
Breaking news reveals a significant shift in American industry. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into U.S. manufacturing is rapidly accelerating, with projections indicating a potential productivity boost of 20% by 2025. This transformative period promises to redefine operational efficiencies and competitive landscapes across the sector.
The AI Imperative: Driving US Manufacturing Forward
The U.S. manufacturing sector is currently undergoing a profound technological evolution, with artificial intelligence at its core. This isn’t merely an incremental upgrade; it is a fundamental re-imagining of production processes, quality control, and supply chain management. The push for AI adoption stems from a global competitive landscape that demands higher efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced innovation.
Recent data from industry analysts underscores the urgency and scale of this integration. Manufacturers are investing heavily in AI-driven solutions to address labor shortages, optimize complex operations, and gain a decisive edge. The forecast 20% productivity gain by 2025 is not just an ambitious target; it reflects a growing consensus among economists and industry leaders on AI’s unavoidable impact.
Key Drivers of AI Adoption
Several factors are converging to accelerate AI integration in American factories. These drivers range from economic pressures to the sheer technological advancements making AI more accessible and powerful than ever before.
- Global Competition: U.S. manufacturers face intense pressure from international competitors, necessitating efficiency gains.
- Labor Shortages: AI and automation help mitigate the impact of skilled labor deficits, ensuring continuous operation.
- Data Explosion: The vast amounts of data generated on factory floors provide fertile ground for AI analytics and insights.
- Cost Reduction: AI optimizes resource allocation, reduces waste, and minimizes downtime, leading to significant cost savings.
Real-World Applications: AI Reshaping Factory Floors Today
AI is no longer a futuristic concept; it is actively being deployed across various facets of U.S. manufacturing, delivering tangible benefits. From precision robotics to sophisticated analytical tools, these applications are demonstrating immediate returns on investment and setting new benchmarks for operational excellence.
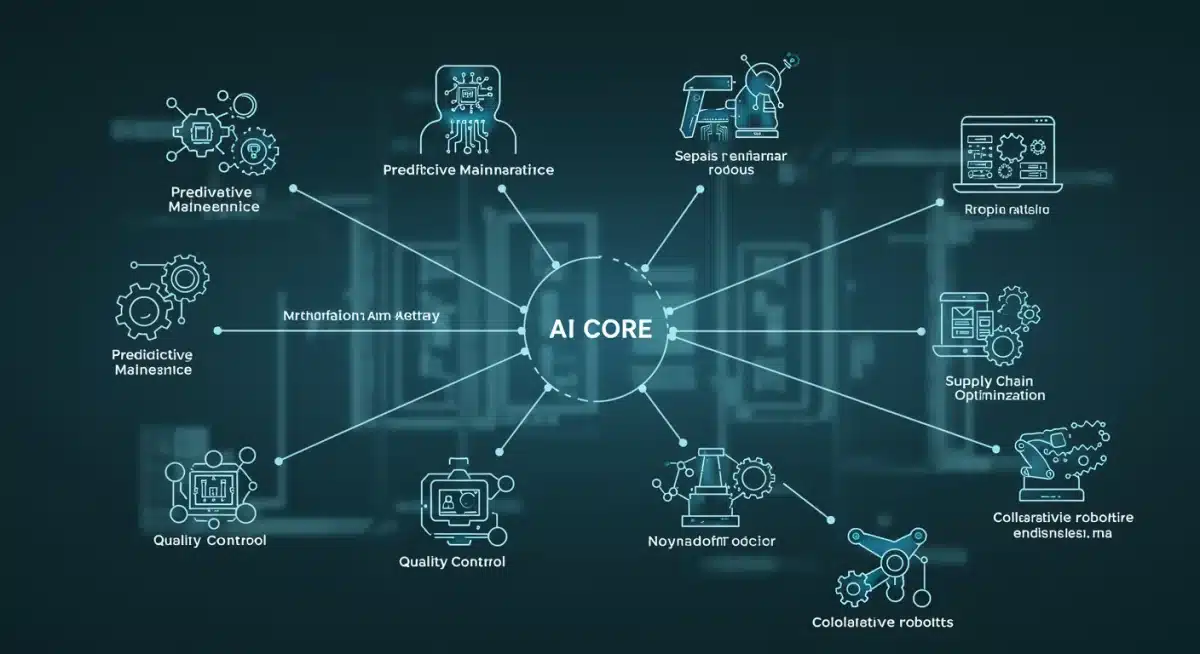
One of the most impactful areas is predictive maintenance. AI algorithms analyze sensor data from machinery to anticipate potential failures before they occur, allowing for proactive repairs and minimizing costly downtime. This shift from reactive to predictive maintenance is saving companies millions annually and vastly improving equipment longevity.
Transforming Quality Control and Supply Chains
AI-powered vision systems are revolutionizing quality control. These systems can inspect products with unparalleled speed and accuracy, identifying defects that human eyes might miss. This results in higher product quality, reduced rework, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Automated Visual Inspection: AI cameras detect minute flaws, ensuring consistent product quality at high speeds.
- Real-time Data Analysis: AI provides immediate feedback on production anomalies, enabling quick adjustments.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI predicts demand fluctuations, optimizes inventory levels, and streamlines logistics, reducing costs and improving responsiveness.
Beyond the factory floor, AI is also optimizing complex supply chains. By analyzing vast datasets, AI can predict demand fluctuations, identify potential bottlenecks, and suggest optimal routing and inventory strategies. This leads to more resilient and cost-effective supply networks, crucial in today’s volatile economic climate.
Economic Impact: The 20% Productivity Boost Explained
The projected 20% productivity boost by 2025 is a staggering figure, representing billions in economic value and a significant enhancement to the U.S. competitive stance. This boost is not merely a theoretical construct but a calculated outcome based on current adoption rates and the proven efficiencies AI brings to manufacturing processes. This increase in output per unit of input will have ripple effects across the economy.
Economists point to several channels through which this productivity surge will manifest. Firstly, automation and optimized processes mean more goods can be produced with the same or fewer resources. Secondly, the reduction in waste and errors directly translates to higher effective output. Thirdly, AI’s ability to accelerate innovation cycles means new, higher-value products can be brought to market faster.
Measuring the Impact
Measuring this 20% boost involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as output per worker, machine uptime, defect rates, and time-to-market for new products. Early adopters of AI are already reporting significant improvements in these metrics, validating the projections.
- Increased Throughput: AI-driven systems can operate continuously and efficiently, leading to higher production volumes.
- Reduced Waste: Precision manufacturing and predictive maintenance minimize material waste and energy consumption.
- Faster Innovation: AI assists in design, simulation, and prototyping, drastically shortening product development cycles.
Challenges and Considerations for AI Integration
While the benefits of AI integration are clear, the path to achieving a 20% productivity boost is not without its challenges. Manufacturers face significant hurdles, including the high initial investment costs, the need for a skilled workforce capable of managing AI systems, and concerns regarding data security and ethical AI deployment.
The capital expenditure required for implementing advanced AI systems, including hardware, software, and integration services, can be substantial. This often creates a barrier for smaller manufacturers, potentially widening the gap between large and small enterprises. Furthermore, the existing workforce requires extensive retraining to adapt to new roles that involve overseeing, maintaining, and developing AI-powered solutions, rather than traditional manual tasks.
Addressing the Hurdles
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach. Government incentives, collaborative industry efforts, and accessible training programs are crucial for widespread AI adoption. Data privacy and cybersecurity also remain paramount, as AI systems often process sensitive operational data.
- Workforce Reskilling: Programs are needed to train employees in AI literacy, data science, and automation management.
- Data Security: Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect proprietary data and AI algorithms from threats.
- Ethical AI: Developing and deploying AI responsibly, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability, is a growing concern.
Government and Industry Collaboration: Fueling the AI Revolution
Recognizing the strategic importance of AI in manufacturing, both government bodies and industry associations are actively collaborating to accelerate its adoption. These partnerships aim to overcome common barriers, foster innovation, and ensure the U.S. remains at the forefront of advanced manufacturing. Initiatives range from funding research and development to creating frameworks for data sharing and standardization.
The U.S. government, through various agencies, is investing in AI research and development centers, providing grants for manufacturers to adopt new technologies, and developing policies that support the growth of the AI ecosystem. Industry consortiums are also playing a vital role by bringing together manufacturers, technology providers, and academic institutions to share best practices and develop common standards.
Strategic Partnerships and Funding
These collaborations are critical for democratizing AI access and ensuring that benefits are not concentrated among a few large corporations. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often lack the resources to individually develop and implement sophisticated AI solutions, making these support structures indispensable.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Government and industry join forces to fund AI research and infrastructure.
- Workforce Development Initiatives: Joint programs to create a pipeline of AI-skilled workers for manufacturing.
- Standardization Efforts: Collaboration on common protocols and interoperability standards for AI systems.
The Future Workforce: Adapting to AI in Manufacturing
The integration of AI will undoubtedly reshape the manufacturing workforce, leading to a shift in required skills and job roles. While some traditional tasks may be automated, new opportunities will emerge in areas such as AI system management, data analysis, robotics maintenance, and human-AI collaboration. The focus is now on upskilling and reskilling the existing workforce to navigate this evolving landscape.
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in training programs that equip employees with the necessary digital competencies. This includes training in data interpretation, machine learning fundamentals, and the operation of advanced robotic systems. The goal is not to replace human workers entirely but to augment their capabilities, allowing them to focus on more complex, creative, and strategic tasks.
Preparing for Tomorrow’s Factory
Educational institutions are also adapting their curricula to meet the demands of an AI-driven manufacturing sector, offering specialized courses and certifications. This proactive approach is vital to ensure a continuous supply of talent capable of designing, deploying, and managing the next generation of smart factories.
- New Job Roles: Emergence of AI specialists, data scientists, robot technicians, and human-AI interaction designers.
- Skill Transformation: Emphasis on critical thinking, problem-solving, digital literacy, and continuous learning.
- Collaborative Environment: Humans and AI systems working in synergy to achieve higher productivity and innovation.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 20% Productivity Boost | Projected increase in U.S. manufacturing efficiency by 2025 due to AI integration. |
| Real-World AI Applications | AI is enhancing predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. |
| Challenges to Integration | High investment costs, workforce reskilling, and data security are key hurdles. |
| Future Workforce | AI will create new job roles and demand advanced digital skills for human-AI collaboration. |
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Manufacturing
The primary benefit is a significant productivity boost, projected at 20% by 2025. This enhancement comes from optimizing production processes, improving quality control, and streamlining supply chain operations through intelligent automation and data analysis, leading to greater output and efficiency.
AI improves quality control through advanced computer vision systems that can detect minute defects with high accuracy and speed. These systems provide real-time feedback, allowing manufacturers to identify and correct issues instantly, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing waste effectively.
Key challenges include substantial initial investment costs for AI infrastructure, the need to reskill the existing workforce for new AI-driven roles, and ensuring robust data security to protect sensitive operational information. Ethical considerations and the complexity of integration are also significant hurdles.
While AI will automate some repetitive tasks, it is generally expected to augment human capabilities rather than replace workers entirely. New roles will emerge in AI system management, data analysis, and human-robot collaboration, requiring a workforce with enhanced digital skills and problem-solving abilities.
Government bodies and industry associations are collaborating through public-private partnerships, funding research and development, and creating workforce development programs. These initiatives aim to provide financial incentives, foster innovation, and establish common standards to facilitate widespread AI integration across the sector.
What Happens Next
The trajectory for AI integration in U.S. manufacturing points towards continued rapid growth. Stakeholders should watch for increased government incentives, expanded industry-led training programs, and the emergence of more accessible, scalable AI solutions tailored for small and medium-sized enterprises. The focus will shift towards refining human-AI collaboration models and establishing robust ethical guidelines, ensuring that the projected productivity gains translate into sustainable economic growth and a more resilient manufacturing base. This ongoing transformation is set to redefine America’s industrial future.