South China Sea: 3 Critical Developments & US Naval Impact (Recent Updates)

Recent developments in the South China Sea have significant, time-sensitive implications for US naval operations, with this article detailing three critical shifts over the past 90 days, providing essential context and analysis for understanding their immediate and future impact.
The South China Sea: 3 Critical Developments in the Last 90 Days and Their Impact on US Naval Operations (TIME-SENSITIVE, RECENT UPDATES) is shaping today’s geopolitical agenda with new details emerging from official statements, satellite intelligence, and regional reports. This update prioritizes what has changed, why these shifts matter, and what to watch next, presenting a clear, factual analysis for our readers.
Escalating Confrontations and Freedom of Navigation Operations
In the past three months, the South China Sea has witnessed a notable uptick in maritime incidents, particularly involving Chinese and Philippine vessels near disputed features. These confrontations have directly tested the resolve of regional actors and prompted increased scrutiny from international observers, including the United States. The frequency and intensity of these encounters signal a heightened state of tension in strategically vital waters.
The US Navy has consistently maintained its presence through Freedom of Navigation Operations (FONOPs), asserting international law in areas claimed by multiple nations. These operations are not merely symbolic; they are concrete demonstrations of Washington’s commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific. The recent escalations have, however, forced a re-evaluation of operational tactics and response protocols for US naval assets operating in close proximity to these flashpoints.
Increased Chinese Coast Guard Aggression
- Water Cannon Incidents: Multiple reports confirm the use of water cannons by Chinese Coast Guard vessels against Philippine resupply missions near Second Thomas Shoal, causing damage and injuries.
- Dangerous Maneuvers: Chinese ships have engaged in increasingly aggressive maneuvers, including blocking and near-collisions, posing significant safety risks to vessels from other claimant states.
- Militia Presence: A growing number of Chinese maritime militia vessels are observed operating in conjunction with official Coast Guard ships, further complicating maritime law enforcement efforts and blurring lines between civilian and state-backed actions.
These actions by Beijing are interpreted by many as an attempt to assert de facto control over disputed territories, challenging the established international order. The consistent harassment of Philippine vessels, particularly those attempting to resupply troops stationed on the BRP Sierra Madre, directly undermines regional stability and international maritime law. This aggressive posture necessitates careful calibration of US responses to avoid unintended escalation while upholding principles of free navigation.
Enhanced US-Philippines Alliance and Joint Drills
A significant development over the last 90 days has been the tangible strengthening of the US-Philippines alliance, directly in response to China’s assertive actions. This renewed partnership is manifesting through expanded joint military exercises, increased defense cooperation, and more explicit diplomatic support from Washington to Manila. The shift indicates a strategic recalibration aimed at bolstering regional deterrence and collective security.
The US and the Philippines have conducted several high-profile joint military exercises, including large-scale naval drills that simulated scenarios in the South China Sea. These exercises are crucial for enhancing interoperability between the two forces, allowing them to coordinate more effectively in potential contingencies. Such drills also send a clear signal to Beijing regarding the depth of the alliance and the commitment to mutual defense.
Key Alliance Strengthening Initiatives
- Balikatan Exercise Expansion: The annual Balikatan exercises have seen an unprecedented scale and scope, incorporating live-fire drills, coastal defense simulations, and multi-domain operations across key strategic locations in the Philippines.
- Access to New Bases: The Philippines has granted the US access to several additional strategically located military bases under the Enhanced Defense Cooperation Agreement (EDCA), significantly improving US force posture and response capabilities in the region.
- Trilateral Cooperation: Discussions and initial steps towards trilateral security cooperation involving the US, Philippines, and Japan, or even Australia, are gaining momentum, aiming to create a more robust multinational framework for maritime security.
This deepening alliance has direct implications for US naval operations. It provides US forces with critical logistical support, staging areas, and intelligence-sharing capabilities closer to potential flashpoints. The ability to operate from Philippine territory reduces response times and enhances the endurance of naval assets, making US presence in the South China Sea more robust and sustained. This strategic advantage is vital for maintaining a credible deterrent in the face of ongoing challenges.
Technological Upgrades and Surveillance Capabilities
The last 90 days have also seen significant advancements in technological deployment and surveillance capabilities by various actors in the South China Sea, influencing the operational environment for US naval forces. Both China and the United States, along with its allies, are investing heavily in advanced maritime domain awareness technologies, creating a more transparent yet potentially more volatile operational space. This technological arms race is reshaping naval strategy and tactical planning.
China continues to expand its network of radar installations, sensor arrays, and surveillance aircraft across its artificial islands and claimed features. These systems provide Beijing with an increasingly comprehensive real-time picture of maritime traffic and foreign military movements. The ability to track vessels and aircraft with greater precision allows China to respond more quickly to perceived infringements and to project its presence more effectively.
Advancements in Maritime Domain Awareness
- Satellite Surveillance: Both sides are leveraging advanced satellite imagery and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) to monitor activities, track vessel movements, and assess infrastructure developments across the vast maritime expanse.
- AI-Powered Analytics: The integration of artificial intelligence into data analysis allows for faster processing of vast amounts of surveillance data, enabling quicker identification of patterns, anomalies, and potential threats.
- Unmanned Systems: The deployment of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) is becoming more prevalent for reconnaissance, surveillance, and even anti-submarine warfare, adding new layers of complexity to naval operations.
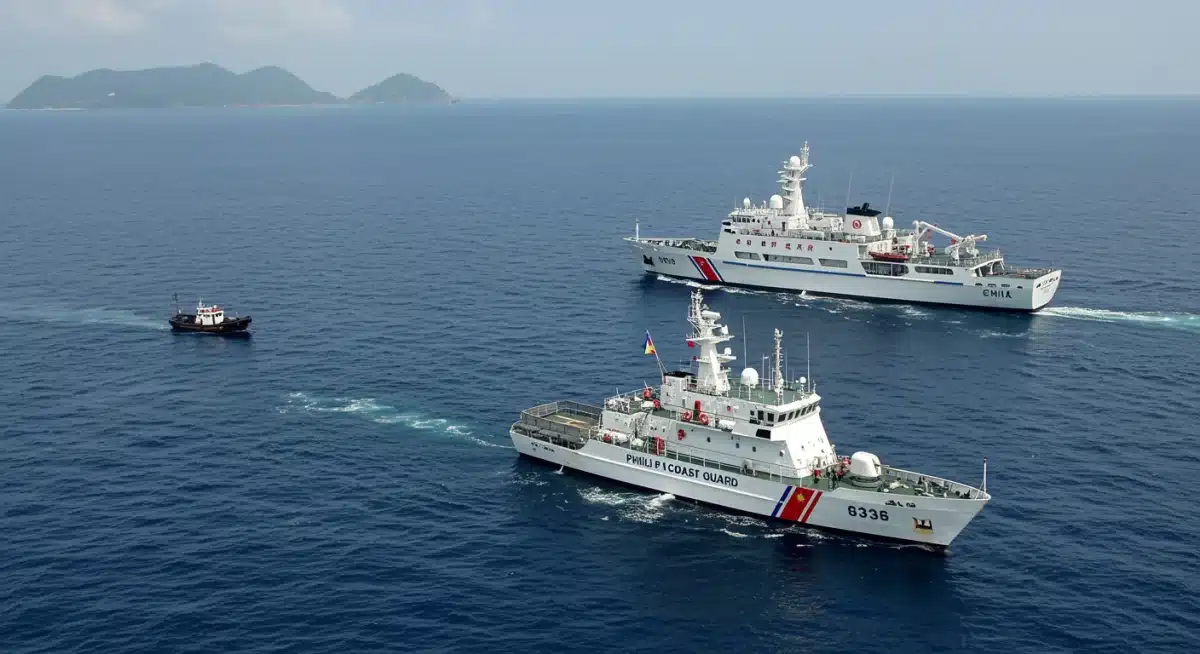

For US naval operations, these technological developments present both challenges and opportunities. Enhanced surveillance means less room for covert operations and a higher risk of detection. However, it also provides US forces and their allies with better situational awareness, improving their ability to anticipate adversary movements and react accordingly. The continuous upgrade of intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) assets is paramount for maintaining a strategic edge and ensuring the safety of naval personnel in this contested environment.
Implications for US Naval Presence and Strategy
The confluence of escalating confrontations, a strengthened US-Philippines alliance, and rapid technological advancements profoundly impacts the US naval presence and strategy in the South China Sea. These developments necessitate a dynamic and adaptable approach from the United States to effectively uphold its interests and commitments in the region. The operational landscape is shifting rapidly, demanding continuous strategic adjustments.
The US Navy’s strategy now focuses on enhancing deterrence through increased forward presence, improved interoperability with allies, and the deployment of advanced capabilities. The goal is to project strength and resolve, ensuring that international law prevails and that freedom of navigation is protected for all nations. This involves not only naval power but also diplomatic and economic tools to influence regional dynamics.
Adapting to the New Geopolitical Reality
- Distributed Maritime Operations: The US Navy is increasingly adopting Distributed Maritime Operations (DMO) concepts, spreading its forces across a wider area to complicate adversary targeting and enhance survivability.
- Integrated Deterrence: A strategy of integrated deterrence combines military, diplomatic, and economic tools to dissuade aggression, leveraging the strengths of allies and partners to create a more formidable front.
- Focus on Resilience: Investments in resilient command and control systems, redundant communication networks, and hardened infrastructure are critical to ensuring sustained operations in a contested environment.
The direct consequence for US naval operations is a heightened state of readiness and a more complex operational calculus. Commanders must balance the need for assertive presence with the imperative to avoid accidental escalation. The increased frequency of encounters with Chinese vessels requires meticulous adherence to rules of engagement and sophisticated de-escalation protocols. Furthermore, the reliance on allies like the Philippines becomes even more critical for shared burden-sharing and collective security.
Economic and Geopolitical Ramifications
The recent developments in the South China Sea extend beyond military and naval operations, carrying significant economic and geopolitical ramifications for the entire Indo-Pacific region and global trade. The stability of these waters is inextricably linked to the prosperity of nations dependent on its vital shipping lanes. Any disruption or escalation carries the potential for widespread economic shockwaves.
The South China Sea is a critical conduit for a substantial portion of global trade, including energy shipments, raw materials, and finished goods. Freedom of navigation through these sea lanes is paramount for the global economy. Any perceived threat to this freedom, whether from military confrontation or unilateral assertions of control, can trigger market instability, increased insurance costs for shipping, and rerouting of vessels, all of which impact global supply chains.
Impact on Regional Economies
- Trade Disruption Risks: Increased tensions raise the specter of trade disruptions, potentially impacting economies heavily reliant on maritime commerce, including key US trading partners in Asia.
- Investment Uncertainty: Geopolitical instability in the region can deter foreign direct investment, as businesses become wary of the risks associated with operating in volatile areas.
- Resource Exploitation: Disputes over fishing rights and hydrocarbon resources, often intertwined with territorial claims, continue to fuel tensions and affect the livelihoods of coastal communities.
From a geopolitical perspective, China’s aggressive posture challenges the foundational principles of international law and the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). The US, through its naval operations and diplomatic efforts, seeks to uphold these principles, fostering a rules-based international order. The outcome of these ongoing tensions will significantly influence the future balance of power in the Indo-Pacific and set precedents for how international disputes are managed globally. The stakes are incredibly high, affecting not just regional security but also global economic stability.
Future Outlook and US Commitments
Looking ahead, the trajectory of events in the South China Sea suggests a continued period of elevated tension and strategic competition. The United States remains steadfast in its commitment to its allies and to the principle of a free and open Indo-Pacific. This commitment will translate into sustained naval presence, continued diplomatic engagement, and adaptive security cooperation initiatives to manage the evolving challenges. The future stability of the region hinges on these ongoing efforts.
The US Navy will likely increase the frequency and complexity of its Freedom of Navigation Operations, ensuring that international waters remain accessible to all nations. These operations, while sometimes perceived as provocative by Beijing, are fundamental demonstrations of international law. Simultaneously, Washington will continue to invest in modernizing its Pacific fleet and developing advanced capabilities tailored to the unique operational environment of the South China Sea. This includes enhancing anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) countermeasures and improving long-range precision strike capabilities.
Anticipated Strategic Adjustments
- Multilateral Engagements: Expect a stronger emphasis on multilateral security dialogues and exercises involving not just treaty allies but also like-minded partners across the Indo-Pacific, such as Australia, Japan, and India.
- Information Warfare Countermeasures: Increased focus on countering disinformation campaigns and enhancing transparency regarding maritime incidents to shape narratives and ensure factual reporting.
- Economic Statecraft: The US will likely leverage economic partnerships and initiatives to reinforce regional stability, offering alternatives to coercive economic practices and strengthening the economic resilience of allies.
The US commitment to its alliances, particularly with the Philippines, will remain a cornerstone of its regional strategy. This involves not only military support but also capacity building, intelligence sharing, and joint development of maritime defense capabilities. The overarching goal is to deter aggression, maintain regional stability, and ensure that all nations can navigate and operate in the South China Sea in accordance with international law. The dynamic nature of these developments requires continuous vigilance and a proactive approach to safeguard peace and prosperity.
| Key Development | Impact on US Naval Operations |
|---|---|
| Escalating Confrontations | Increased risk of incidents, requiring refined FONOPs and de-escalation protocols. |
| Enhanced US-Philippines Alliance | Improved interoperability, logistical support, and strategic access for US forces. |
| Technological Upgrades | Higher situational awareness but also increased detection risks; demands advanced ISR. |
| Geopolitical Ramifications | Challenges to international law, impacting global trade and regional balance of power. |
Frequently Asked Questions About South China Sea Dynamics
Over the last 90 days, we’ve seen escalating maritime confrontations, particularly between Chinese and Philippine vessels, a significant strengthening of the US-Philippines alliance through joint drills, and rapid advancements in surveillance and military technology by all key regional actors.
US naval operations face increased risks during freedom of navigation operations, benefit from enhanced interoperability and logistical support via the Philippine alliance, and must contend with a more complex, technologically advanced surveillance environment, requiring adaptive strategies.
The alliance provides critical strategic access for US forces, improves their response capabilities in the South China Sea, and enhances collective deterrence through expanded joint military exercises, signaling a unified front against regional aggression.
Yes, increasing tensions and potential for conflict in the South China Sea raise concerns about the stability of vital shipping lanes. This instability could lead to trade disruptions, increased shipping costs, and impact global supply chains, affecting economies worldwide.
The US strategy involves a sustained naval presence, conducting Freedom of Navigation Operations, strengthening alliances, investing in advanced military capabilities, and engaging in multilateral diplomatic efforts to uphold international law and ensure a free and open Indo-Pacific.
What this means for the Future of the South China Sea
The escalating military presence and diplomatic maneuvering in the South China Sea signal not just a regional dispute, but a defining test for the future of international maritime norms and strategic power projection. With the United States intensifying its naval presence and reinforcing security ties with regional partners, the South China Sea is evolving into a critical arena where influence, deterrence, and territorial claims intersect.
Analytical resources like the Global Conflict Tracker provide a clear overview of the evolving tensions and territorial disputes shaping this region, offering a valuable lens through which to interpret each new strategic move — veja mais nesta referência sobre os conflitos no South China Sea. As joint military exercises expand and surveillance technologies grow more sophisticated, each deployment, each diplomatic declaration, and each freedom-of-navigation operation becomes a signal with global implications.
What lies ahead is a period where perception and signaling will be just as critical as physical control of maritime routes. The South China Sea will remain a geopolitical barometer — reflecting not only the balance of power in Asia but the future credibility of international law itself.